Animal Cell Mitochondria Biography
Source:- Google.com.pk
Cell Structure[edit]
Cell Organelles[edit]
Organelles are parts of cells. Each organelle has a specific function.
1. Nuclear membrane 2. Nuclear pore 3. Rough endoplasmic reticulum (REM) 4. Smooth endoplasmic reticulum 5. Ribosome attached to REM 6. Macromolecules 7. Transport vesicles 8. Golgi apparatus 9. Cis face of Golgi apparatus 10. Trans face of Golgi apparatus 11. Cisternae of Golgi apparatus 12. Secretory vesicle 13. Cell membrane 14. Fused secretory vesicle releasing contents 15. Cell cytoplasm 16. Extracellular environment
Nucleus[edit]
Description:
Largest organelle
Surrounded by a nuclear envelope, which contains pores (holes)
Contains chromatin and the nucleolus
Function:
Store the genetic material
Controls the cell's activities
Pores allow substances to move between the nucleus and the cytoplasm
The nucleolus makes ribosomes (see below)
The parts of a cell nucleus
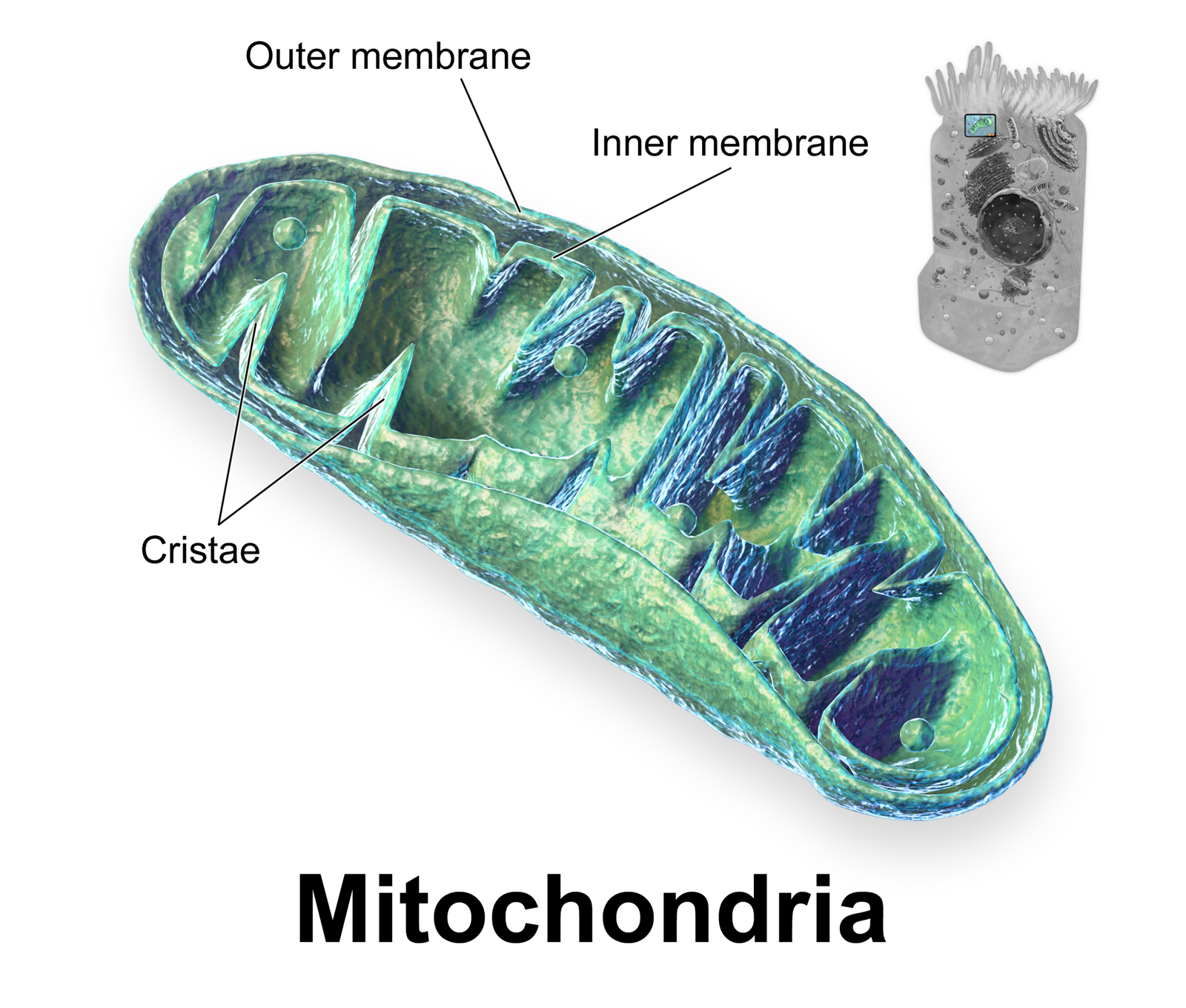
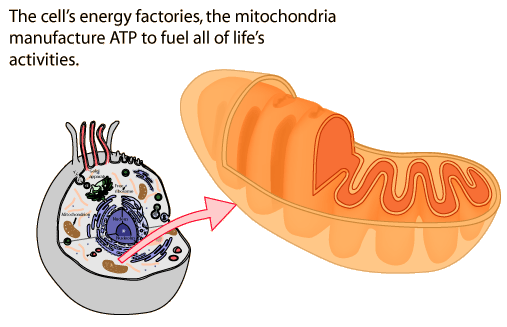
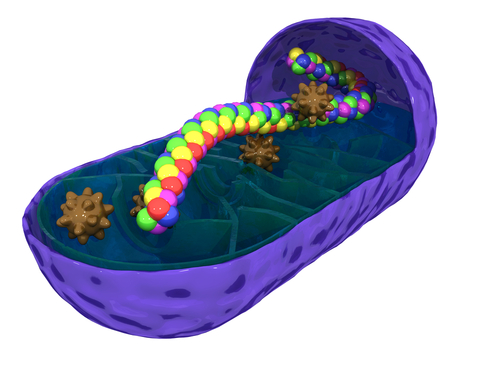
Mitochondria[edit]
Description:
Oval shaped
They have a double membrane - the inner one is folded to form structures called cristae
Inside is the matrix, containing enzymes
Function:
They are the site of aerobic respiration
Makes energy in the form of ATP (adenosine triphosphate) as a source of energy for the cell's activities
Cristae give a bigger surface area so more enzymes can fit in
The diagram shows a section of a eukaryotic cell's mitochondrion.
Endoplasmic Reticulum[edit]
Description:
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum is a system of membranes which enclose a fluid-filled space
Rough endoplasmic reticulum is similar, but covered in ribosomes
Function:
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum synthesises and processes lipids
Rough endoplasmic reticulum folds and processes proteins that have been made at the ribosomes, transports proteins around the cell.
Golgi Apparatus[edit]
Description:
A group of fluid-filled, flattened sacs
Function:
Processes and packages new lipids and proteins
Once finished, it makes vesicles which transport the molecules to the edge of the cell for ejection
Makes lysosomes
Ribosome[edit]
Description:
Very small
Either floats free in the cytoplasm or is attached to rough endoplasmic reticulum
Function:
The site where protein synthesis takes place
Lysosome[edit]
Description:
Round
No clear internal structure
Function:
Contains digestive enzymes which can be used to digest invading cells or break down worn-out organelles (autolysis)
Microvilli[edit]
Description:
These are folds in the plasma membrane
Found in cells involved in absorption
Stereotypically found on the villi in the small intestine
Function:
Increase the surface area of the plasma membrane
Plasma Membrane[edit]
Found on the surface of animal cells, it's mainly made of lipids and proteins. It controls the movement of substances in and out of the cell; further explanation can be found later in this book.
Chloroplast[edit]
Description:
Found in plant cells only
Inner membrane is folded to form stacks of grana
Molecules of chlorophyll are on the grana
Function:
Chlorophyll captures photons of light used for photosynthesis
Chloroplast-new.jpg
Animal cell diagram
Plant cell diagram
Refer to the below table for the differences between plant and animal cells.
Table 1: Comparison of structures between animal and plant cells
Typical animal cell Typical plant cell
Organelles
Nucleus
Nucleolus (within nucleus)
Rough endoplasmic reticulum (ER)
Smooth ER
Ribosomes
Cytoskeleton
Golgi apparatus
Cytoplasm
Mitochondria
Vesicles
Lysosome
Centrosome/Centrioles
Many small vacuoles
Nucleus
Nucleolus (within nucleus)
Rough ER
Smooth ER
Ribosomes
Golgi apparatus
Cytoplasm
Mitochondria
Vesicles
Chloroplast
One large vacuole
Additional structures
Plasma membrane
Cilia
Plasma membrane
Cell wall
Plasmodesmata
Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes[edit]
Eukaryotic cells are complex, and include all animal and plant cells. Prokaryotic cells are smaller and simpler, like bacteria.
The table below is a comparison of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells:
Animal Cell Mitochondria Animal Cell Model Diagram Project Parts Structure Labeled Coloring and Plant Cell Organelles Cake


Animal Cell Mitochondria Animal Cell Model Diagram Project Parts Structure Labeled Coloring and Plant Cell Organelles Cake


Animal Cell Mitochondria Animal Cell Model Diagram Project Parts Structure Labeled Coloring and Plant Cell Organelles Cake

Animal Cell Mitochondria Animal Cell Model Diagram Project Parts Structure Labeled Coloring and Plant Cell Organelles Cake


Animal Cell Mitochondria Animal Cell Model Diagram Project Parts Structure Labeled Coloring and Plant Cell Organelles Cake

Animal Cell Mitochondria Animal Cell Model Diagram Project Parts Structure Labeled Coloring and Plant Cell Organelles Cake


Animal Cell Mitochondria Animal Cell Model Diagram Project Parts Structure Labeled Coloring and Plant Cell Organelles Cake


Animal Cell Mitochondria Animal Cell Model Diagram Project Parts Structure Labeled Coloring and Plant Cell Organelles Cake

Animal Cell Mitochondria Animal Cell Model Diagram Project Parts Structure Labeled Coloring and Plant Cell Organelles Cake


Animal Cell Mitochondria Animal Cell Model Diagram Project Parts Structure Labeled Coloring and Plant Cell Organelles Cake


Animal Cell Mitochondria Animal Cell Model Diagram Project Parts Structure Labeled Coloring and Plant Cell Organelles Cake
No comments:
Post a Comment