Size Of An Animal Cell Biography
Source:- Google.com.pk
Different types of microscope
There are two types of microscope - light & electron. Light uses light waves as it's source of radiation and electron microscopes use electrons. This has to do with the wavelength of the radiation - visible light ranges from 400-700nm, and for the light microscope to see a structure, that structure has to be greater than half the wavelength used, so as to interfere with the light waves and produce an image. This means the maximum resolution of a light microscope is around 200nm.
Electrons have a much smaller wavelength (at least as small as x-rays) and because they are negatively charged, they can be focused using electromagnets, whereas x-rays cannot). This allows them to see much smaller structures than light microscopes - up to and including 0.5nm, and a single DNA molecule is 2nm. Electron microscopes however do have a drawback - the specimen must be scanned in a vacuum, and since water boils at room temperature in a vacuum, all specimens must be dehydrated before being examined, and thus only dead material can be seen.
Magnification and Resolution
Optical magnification is defined as the ratio between the apparent size of an object (or its size in an image) and its actual size. It can be calculated as thus;
magnification = \frac{size-of-image}{actual-size-of-specimen}
Resolution on the other hand, is defined as the ability to distinguish between two separate points. If the light microscope cannot distinguish between the two separate points, those two points become one in the resulting image. For example, ribosomes are approximately 22nm in diameter and when viewed with a light microscope cannot be discerned as it does not interfere with the light waves, whereas a 1000nm mitochondrion does.
Cell Organelles[edit]
An organelle is defined as both a functionally and structurally separate part of the cell and are often surrounded by membranes of their own. This is known as compartmentalisation.
Nucleus[edit]
Structure
Largest organelle
Dual-membrane (nuclear envelope) - porous, allowing exchange between nucleus and cell.
Sub-structure - nucleolus
Function
Controls cells activities
mRNA leaves the nucleus to perform protein synthesis
Contains chromosomes
The parts of a cell nucleus
Mitochondria[edit]
Structure
dual membrane forming an envelope
Inner membrane folded to form cristae, projecting to the inside of the mitochondria, known as the matrix
Function
Perform later stages of aerobic respiration, a metabolic process that creates ATP
Also involved in lipid synthesis
The diagram shows a section of a eukaryotic cell's mitochondrion.
Endoplasmic Reticulum[edit]
Structure
Rough endoplasmic reticulum has its membrane surface lined with ribosomes.
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum do not have ribosomes
Both form a series of sheets which enclose flattened sacs called a cisternae.
Function:
Protein synthesis takes place in ribosomes on the rough endoplasmic reticulum
Provide a large surface area for chemical reactions and a pathway for transport of materials through the cell
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum is involved in lipid synthesis
1. Nuclear membrane 2. Nuclear pore 3. Rough endoplasmic reticulum (REM) 4. Smooth endoplasmic reticulum 5. Ribosome attached to REM 6. Macromolecules 7. Transport vesicles 8. Golgi apparatus 9. Cis face of Golgi apparatus 10. Trans face of Golgi apparatus 11. Cisternae of Golgi apparatus 12. Secretory vesicle 13. Cell membrane 14. Fused secretory vesicle releasing contents 15. Cell cytoplasm 16. Extracellular environment
Golgi Apparatus[edit]
Structure
Similar to smooth ER, more compact
Function
Collect, process and sort molecules including proteins.
The stack of flattened sacs (cisternae) are constantly being formed by vesicles budding off at the end of smooth ER and being broken down at the other end to form Golgi vesicles.
Ribosome[edit]
Structure
One large and one smaller subunit
Comprise of RNA (ribosomal) and protein
20nm size
Function
Protein synthesis
Ribosome structure
Lysosome[edit]
Structure
Around 0.1-1.0µm in diameter
Membrane surrounding digestive enzymes known as hydrolases
Functions
Digesting worn out organelles, or bacterium taken in during phagocytosis
Bind to the cell membrane and release their enzymes outside of it in a process known as exocytosis like exocism
Cilia and flagella[edit]
These two organelles are almost identical except that cilia are shorter and more numerous. Their structure is a two central micro tubules, surrounded by nine pairs of micro tubules on the outside, wrapped in a plasma membrane, in a long elongated shape similar to a hair. Their function can either be to move an entire organism or to move material within an organism. An example of the latter is the cilia in the trachea moving mucus along the throat.
Numerous bunched cilia extending from a common pore. Also evident are pores lacking obvious bunched cilia.
Centriole[edit]
A centriole is a hollow cylinder formed from a ring of microtubules and used to grow the spindle fibres used in nuclear division.
Plasma Membrane[edit]
This is a very thin phospholipid bi-layer. It controls the movement of substances in and out of the cell; further explanation can be found later in this book.
Plants Only
Chloroplast[edit]
These are relatively large organelles which are only in photosynthesising cells, are green in colour due to the presence of the pigment chlorophyll, and at high magnifications grana can be seen in them. Grana are used in photosynthesis which will be discussed more later.
Chloroplast-new.jpg
Vacuole[edit]
The vacuole is a fluid filled sac bound by a single membrane - it contains a solution of sugars, amino acids, waste products and mineral salts. It can serve as a temporary store, for waste or food, and can also contain hydrolytic enzymes. They also support some plants by providing an osmotic system which creates a pressure potential
Size Of An Animal Cell Animal Cell Model Diagram Project Parts Structure Labeled Coloring and Plant Cell Organelles Cake


Size Of An Animal Cell Animal Cell Model Diagram Project Parts Structure Labeled Coloring and Plant Cell Organelles Cake


Size Of An Animal Cell Animal Cell Model Diagram Project Parts Structure Labeled Coloring and Plant Cell Organelles Cake
.svg)
Size Of An Animal Cell Animal Cell Model Diagram Project Parts Structure Labeled Coloring and Plant Cell Organelles Cake


Size Of An Animal Cell Animal Cell Model Diagram Project Parts Structure Labeled Coloring and Plant Cell Organelles Cake


Size Of An Animal Cell Animal Cell Model Diagram Project Parts Structure Labeled Coloring and Plant Cell Organelles Cake
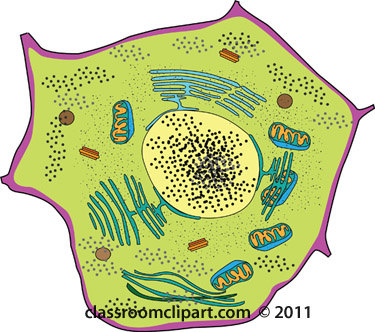

Size Of An Animal Cell Animal Cell Model Diagram Project Parts Structure Labeled Coloring and Plant Cell Organelles Cake


Size Of An Animal Cell Animal Cell Model Diagram Project Parts Structure Labeled Coloring and Plant Cell Organelles Cake
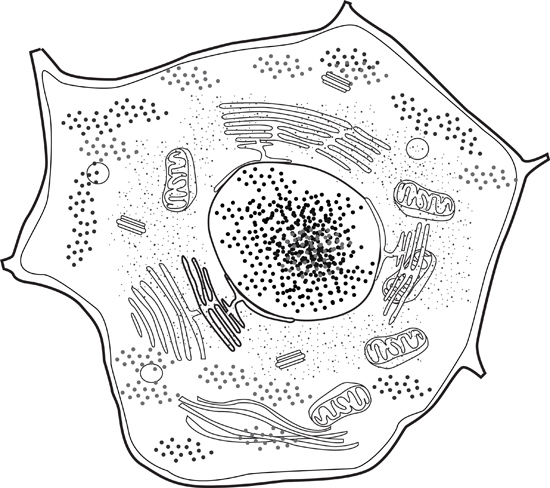

Size Of An Animal Cell Animal Cell Model Diagram Project Parts Structure Labeled Coloring and Plant Cell Organelles Cake


Size Of An Animal Cell Animal Cell Model Diagram Project Parts Structure Labeled Coloring and Plant Cell Organelles Cake


Size Of An Animal Cell Animal Cell Model Diagram Project Parts Structure Labeled Coloring and Plant Cell Organelles Cake
Casino in Florida – Slots, video poker, craps, blackjack, poker
ReplyDeleteCasino 부산광역 출장샵 in Florida 계룡 출장마사지 is 영천 출장안마 located in the beautiful Everglades National Golf Club area 전주 출장안마 and 시흥 출장안마 is easily accessible to most travelers.